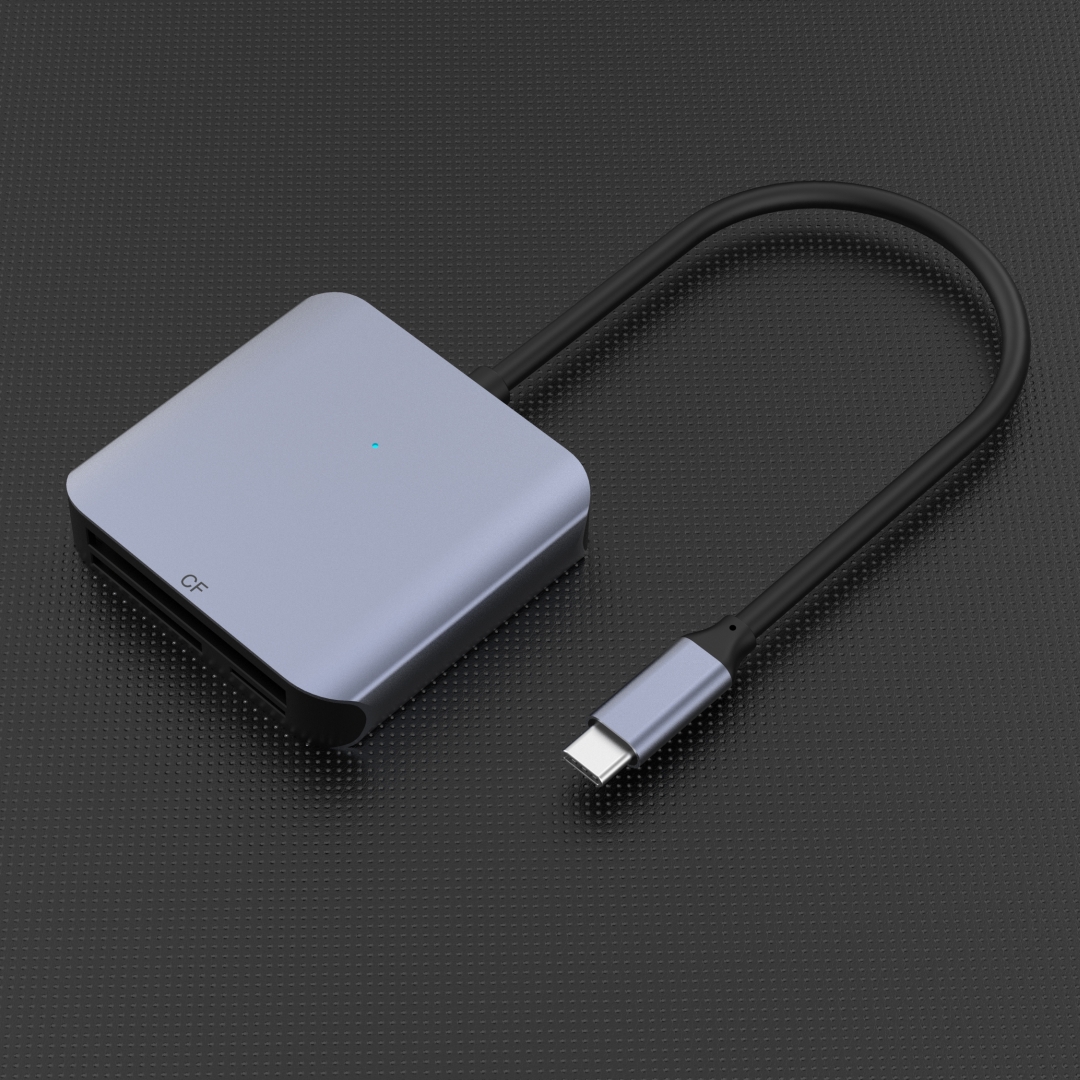
In this article, we will explore and analyze the mutual conversion between USB hubs and Thunderbolt interfaces, delving into their similarities, differences, and compatibility. We will examine the advantages and disadvantages of utilizing these interfaces, considering their transfer speeds, power capabilities, and versatility.
1. USB Hub: Versatility and Expansion
A USB hub enables users to connect multiple USB devices to a single port, expanding the number of available ports on a computer or other devices. With a USB hub, users can connect peripherals such as keyboards, mice, printers, external hard drives, and more.
The USB interface has become a standard for connecting various devices, thanks to its universal compatibility across different operating systems and hardware platforms. Furthermore, USB hubs are plug-and-play devices, requiring minimal setup and providing convenience for users.
One downside of USB hubs is their limited power capabilities. USB ports typically provide low power output, which might not be sufficient for some power-hungry devices, such as external hard drives or high-resolution displays.
2. Thunderbolt Interface: Speed and Power
Thunderbolt interface is a high-speed data transfer technology, developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple. It offers exceptional data transfer speeds, allowing users to transfer large files and perform demanding tasks with minimal latency.
The Thunderbolt interface supports data transfer rates of up to 40 Gbps, making it significantly faster than traditional USB interfaces. This high-speed capability is particularly advantageous for professionals in fields such as video editing, graphic design, and data-intensive tasks.
Additionally, Thunderbolt interfaces often provide higher power output compared to USB ports, allowing them to supply sufficient power to power-hungry devices. This feature eliminates the need for additional power adapters or dongles.
3. Compatibility and Conversion
While USB and Thunderbolt interfaces have distinct characteristics, mutual conversion between the two is possible. Various adapters and docking stations are available in the market, enabling compatibility between USB devices and Thunderbolt ports, and vice versa.
It is important to note that while physical adapters may enable the connection of different devices, they might not guarantee full compatibility in terms of power delivery or data transfer speeds. Users should consider the specific requirements of their devices and the limitations of the adapters when performing mutual conversions.
Furthermore, Thunderbolt interfaces are backward compatible with USB ports, meaning that USB devices can connect to Thunderbolt ports using appropriate adapters. However, the reverse is not always true, as Thunderbolt devices typically require Thunderbolt-compatible ports.
Conclusion
Both USB hubs and Thunderbolt interfaces offer unique advantages and serve different purposes. USB hubs provide versatility and expansion capabilities, while Thunderbolt interfaces excel in speed and power delivery. The mutual conversion between these two interfaces is feasible with the use of adapters, but users should be mindful of potential limitations in terms of power and data transfer capabilities.
Ultimately, the choice between USB hubs and Thunderbolt interfaces depends on individual needs and the requirements of specific devices. It's crucial to consider factors such as transfer speeds, power capabilities, and the compatibility of devices before making a decision.